
Understanding PCBA Assembly: A Comprehensive Guide to the Electronics Manufacturing Process
2025-08-12
Understanding PCBA Assembly: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to PCBA
2. The Importance of PCBA in Electronics Manufacturing
3. Key Components Involved in PCBA Assembly
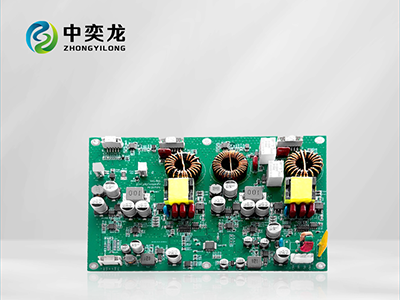
3.1 Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
3.2 Electronic Components
3.3 Soldering Materials
4. The PCBA Process: Step-by-Step Breakdown
4.1 Design and Prototyping
4.2 Component Placement Techniques
4.3 Soldering Methods: Through-Hole vs. Surface Mount
4.4 Testing and Quality Assurance
5. Advantages of Using PCBA
6. PCBA Industry Trends and Innovations
7. Common Challenges in PCBA Assembly
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
9. Conclusion
1. Introduction to PCBA
Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) is a critical process in the electronics manufacturing industry. It is where the electronic components are mounted and connected to a circuit board, forming the foundation for various electronic devices. From consumer electronics to industrial applications, PCBA plays a vital role in ensuring that the devices function effectively and reliably. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the PCBA assembly process, its components, and its significance in the broader context of electronics manufacturing.
2. The Importance of PCBA in Electronics Manufacturing
PCBA is at the heart of all electronic devices. The assembly process allows manufacturers to create complex circuitry tailored to specific applications. The significance of PCBA can be attributed to several factors:
- **Efficiency**: Automated assembly processes ensure that PCBA can be completed quickly and accurately, reducing lead times.
- **Scalability**: The PCBA process can easily scale from small prototypes to large production runs, accommodating various business needs.
- **Cost-Effectiveness**: By optimizing the assembly process, manufacturers can minimize waste and reduce costs, leading to more competitive pricing for end products.
- **Quality Assurance**: Rigorous testing protocols during the PCBA process ensure that the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations.
3. Key Components Involved in PCBA Assembly
A successful PCBA process relies on several key components that work together seamlessly. Understanding these components is crucial for anyone involved in electronics manufacturing.
3.1 Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
The PCB serves as the backbone of the assembly. It provides the physical structure and electrical connections for the electronic components. PCBs come in various types, including single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer boards, each catering to specific applications and complexities.
3.2 Electronic Components
Numerous electronic components are incorporated into PCBA, ranging from resistors and capacitors to integrated circuits and connectors. Each component plays a unique role in the functionality of the final product.
3.3 Soldering Materials
Soldering is the process of joining electronic components to the PCB, and the choice of soldering material is critical. Lead-based and lead-free solder are commonly used, with an increasing trend towards lead-free options due to environmental concerns.
4. The PCBA Process: Step-by-Step Breakdown
The PCBA process involves a series of meticulously planned steps to ensure quality and efficiency.
4.1 Design and Prototyping
The first step in PCBA is the design phase, which includes creating schematic diagrams and PCB layouts. Prototyping allows manufacturers to test the design before moving into full production, identifying and fixing potential issues.
4.2 Component Placement Techniques
Once the PCB is designed, the next step is component placement. This can be achieved through manual placement or automated pick-and-place machines, which can significantly increase assembly speed and accuracy.
4.3 Soldering Methods: Through-Hole vs. Surface Mount
Two primary soldering methods are used in PCBA: through-hole and surface mount.
- **Through-Hole Soldering**: Involves inserting component leads into holes drilled in the PCB, providing strong mechanical connections.
- **Surface Mount Soldering**: Components are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB, allowing for more compact designs and higher component density.
4.4 Testing and Quality Assurance
After soldering, thorough testing is conducted to ensure the assembly meets quality standards. Techniques such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and Functional Testing are employed to identify defects and confirm functionality.
5. Advantages of Using PCBA
Implementing PCBA offers numerous advantages for manufacturers, including:
- **Enhanced Performance**: Optimized layouts and high-quality components lead to better device performance.
- **Reduced Production Time**: Automated processes streamline assembly, significantly reducing time to market.
- **Improved Reliability**: Consistent quality assurance protocols ensure that products are reliable and meet consumer expectations.
- **Flexibility**: The ability to quickly adapt to changes in design or component specifications allows manufacturers to remain competitive.
6. PCBA Industry Trends and Innovations
The PCBA industry is continually evolving, driven by technological advancements and market demands. Key trends include:
- **Miniaturization of Components**: Smaller, more powerful components are being developed, allowing for more compact designs.
- **Increased Use of Automation**: Robotics and AI are being integrated into the assembly process to enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
- **Sustainability Initiatives**: Many manufacturers are adopting environmentally friendly practices, including the use of lead-free solder and reducing waste.
7. Common Challenges in PCBA Assembly
While the PCBA process is essential, it also comes with its challenges:
- **Component Sourcing**: Finding reliable suppliers for components can be time-consuming and costly.
- **Quality Control Issues**: Maintaining consistent quality across production batches is crucial but can be challenging.
- **Cost Management**: Balancing quality and cost can be difficult, especially in a competitive market.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between through-hole and surface mount technology in PCBA?
A1: Through-hole technology involves inserting component leads into holes on the PCB, providing strong connections. Surface mount technology places components directly onto the PCB surface, allowing for higher component density and smaller designs.
Q2: How can quality assurance be ensured during the PCBA process?
A2: Implementing rigorous testing protocols, including Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and Functional Testing, helps ensure that each assembly meets quality standards.
Q3: What are some common applications of PCBA?
A3: PCBA is used in a wide range of applications, including consumer electronics (smartphones, TVs), industrial equipment, automotive systems, and medical devices.
Q4: Why is lead-free solder becoming more popular in PCBA?
A4: Lead-free solder is less harmful to the environment and poses fewer health risks, leading to increased demand for sustainable practices in electronics manufacturing.
Q5: What are the benefits of outsourcing PCBA assembly?
A5: Outsourcing can reduce costs, improve access to advanced technology, and allow companies to focus on core competencies while leveraging the expertise of specialized PCB manufacturers.
9. Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of PCBA assembly is essential for anyone involved in the electronics manufacturing industry. From its significance in creating reliable devices to the intricate processes that ensure quality, PCBA remains a critical aspect of modern technology. By staying informed about industry trends and overcoming common challenges, manufacturers can enhance their assembly processes and deliver superior products to the market. As we look to the future, the evolution of PCBA will undoubtedly continue to shape the landscape of electronics manufacturing, offering exciting opportunities for innovation and growth.
Related News











 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
 E-mail
E-mail